1. Introduction
1.1. Labour Pain and Anxiety
Childbirth is painful, and the pain usually begins during the latent stage of vaginal labour (the period from when the mother’s cervix begins to soften and dilate) and continues to intensify during the established phase (where cervical dilation has reached 4 cm), up until the child is born [1]. Whilst labour pain is a multifaceted and subjective phenomenon, for most women it is the most extreme form of pain that they will endure and may lead to negative physiological and psychological outcomes [2,3]. Excessive increases in physiological factors, including the mother’s heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP), oxygen intake, and respiratory rate (RR) have been shown to have negative effects on the mother and unborn child [3,4]. Consequently, unbearable, unalleviated labour pain can lead to extreme exhaustion, mental distress, anxiety, and cognitive dysfunction in the mother [3]. Anxiety and distress activate the sympathetic nervous system by increasing the secretion of hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline into the bloodstream, which can obstruct oxytocin secretion [5]. Consequently, contractions may change in pattern, decrease in rate, or discontinue entirely [1], thus affecting labour progression and increasing the risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) being performed [6,7]. These hormonal changes can also reduce blood supply to the uterus, therefore impacting foetal oxygen levels and putting the unborn child in danger [1,8]. While labour pain is a crucial indicator of childbirth, it should be effectively managed to prevent obstetric difficulties and the need for further medical interventions.
1.2. Caesarean Section and Anxiety
An alternative method for childbirth is a C-section i.e., the surgical removal of the baby and placenta from the mother’s abdominal and uterine wall [9]. Women undergoing C-sections are likely to experience elevated levels of psychological anxiety, as despite it being a common surgical procedure, there is a higher risk in comparison to vaginal delivery due to the potential complications, including blood loss, laceration infection, endometriosis, venous thromboembolism, collapsed lungs, and thrombophlebitis [9,10]. Perioperative anxiety can be defined as a distressing and unpleasant feeling causing worry and nervousness throughout the preoperative, operative, and postoperative period that creates an emotional reaction to a possible threat [11,12]. Perioperative anxiety has physiological implications as the sympathetic adrenal–medullary system becomes aroused, which in turn may affect the circulatory system, leading to an increased risk of complications, including constriction of the mother’s coronary arteries, greater blood viscosity, and increased risk of a heart attack [13]. It is therefore crucial that heightened anxiety is detected and managed throughout the perioperative period, as an inability to do so may delay recovery, increase hospital admission length, and intensify maternal pain sensitivity, leading to a greater demand for pain-relieving drugs [14,15]. Research by Wyatt et al. [16] revealed that a substantial proportion of anxious women took benzodiazepines pre-surgery to manage their anxiety despite knowing the negative side effects associated with the drug, for example, respiratory depression, indicating a need to consider alternative forms of anxiety management with greater risk aversion for women undergoing C-sections.
1.3. Music-Based Interventions for Pain and Anxiety Management
The management of pain and anxiety during vaginal labour and C-sections is a critical worry for the mother and healthcare professionals [17]. The most common and successful methods of pharmacological pain relief during childbirth include epidural analgesia, nitrous oxide, and intravenous opioids [18]. However, these methods come with unwanted potential side effects. These include affecting the mother’s sensations of control, hindering labour progression, increasing the probability of additional interventions, including C-section [19], inducing drowsiness, and impacting the mother’s ability to safely breastfeed her baby [19]. Delivering alternative non-pharmacological treatments that grant the mother independence and active choice over pain management during childbirth can in turn lower anxiety and fear [20].
Music-based interventions are methods of non-pharmacological pain relief that have received increased interest in recent years [8]. Music is ever-present, emotive, social, and in its most elective form, occurs in every culture [21]. The history of music and its therapeutic role within the medical field has been discussed and reported on as far back as 4000 BC [21]. A variety of music-based therapies, strategies, and methods may be beneficial for promoting health and well-being [22].
Many scientific articles report the therapeutic value of music-based interventions during childbirth [23,24,25,26]. Music can positively affect the physiology of mothers during labour by activating the primary auditory cortex, which further stimulates the limbic system, brain stem, hypothalamus, and cerebral cortex. As the auditory cortex and the pain centre of the cerebral cortex are neighbouring, and thus highly connected, music can activate endorphin secretion, increase oxygenation in organs and tissues, and reduce pain sensitivity [27].
Previous systematic reviews have already summarised the effect of music on pain and anxiety during labour and C-section [28,29,30,31]. However, two of these reviews included studies with multiple research designs e.g., quasi-experimental designs, with a risk of potential bias due to the absence of randomisation [28,29]. One systematic review examined the effect of music on anxiety in mothers during C-sections only [31] and another assessed the use of music exclusively for anxiety during labour [30]. As the use of non-pharmacological interventions continues to gain popularity [8], and novel studies have recently been published, an updated systematic review seems timely.
To the best of our knowledge, no systematic review has specifically focused on randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that tested the effects of music-based interventions for anxiety and pain management during both vaginal labour and caesarean sections. RCTs are considered the gold standard for effective research, as randomisation limits bias, allowing researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships between an intervention and an outcome [32]. Since the therapeutic use of music and music therapy are considered a physically non-invasive, generally cost-effective, natural intervention with limited side effects [8,33], policymakers and healthcare officials should seriously consider its place during childbirth so that women can make educated and informed decisions regarding their birth preferences using the current evidence available.
1.4. Aims and Objectives
This systematic review aims to summarise and evaluate the available literature on the effects of music-based interventions for pain and anxiety management during vaginal labour and caesarean delivery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The present systematic review was conducted in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [34]. shows the completed PRISMA checklist for this systematic review. After preliminary scoping searches in March 2023, PsychInfo (Ovid), PubMed, and Web of Science were selected to obtain studies for this review.
The general search terms were:
- Birth, labour, childbirth
- Caesarean birth, caesarean section
- Music intervention, music therapy
However, we made adaptations for these general search terms according to the requirements of each electronic database as explained below.
The search criteria for each electronic database used the appropriate keywords and MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) for labour and music-based interventions. Boolean operators, truncation, wildcards, and proximity searches were included to increase the sensitivity and comprehensiveness of the search [35]. No limits were applied to the search. Due to extensive database coverage, no additional hand-searching was conducted. The following search terms were used: PsychInfo (Ovid): birth/or caesarean birth/or “labor (childbirth)”/or natural childbirth/or birth or caesarean birth or caesarean section or cesarean birth or cesarean section or C-section or childbirth AND music intervention* or music-based intervention* or music therap* or music therapy/or (effect* adj2 music-based intervention*) or (effect* adj2 music intervention*) or (effect* adj2 music therap*); Web of Science: (ALL = (birth* or childbirth or labo$r or “c*sarean birth” or “c*sarean section” or “c-section” or “natural birth” or parturition)) AND ALL = (“music-based intervention*” OR “music therap*” OR “music intervention”); PubMed: (“Parturition”[Mesh] OR “Natural Childbirth”[Mesh] OR “Cesarean Section”[Mesh] OR birth[Title/Abstract] OR natural birth*[Title/Abstract] OR labour[Title/Abstract] OR labor[Title/Abstract] OR childbirth[Title/Abstract] OR “caesarean section” OR “caesarean birth” OR “cesarean birth” OR C-section) AND (“music-based intervention*”[Title/Abstract] OR “music intervention*”[Title/Abstract] OR “music therap*”[Title/Abstract] OR “Music Therapy”[Mesh]).
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria were created and confirmed based on published guidance how to write systematic reviews [36]. This included the following:
2.3. Study Selection and Risk of Bias
The title and abstracts of studies obtained through the searches were imported into EndNote and duplicates were removed using the software. Articles were then imported into Rayyan to detect and remove further duplications.
A two-step screening method involving a preliminary title and abstract screening, followed by a thorough full-text screening was implemented. Two independent reviewers (ARH and DG) screened the title and abstracts against the prespecified eligibility criteria outlined above. During the second stage, the first reviewer hand-selected significant information from each included paper, including bibliographic information, sociodemographic information, study design, measurement instruments, types of interventions, main results, and statistical significance. Both reviewers (ARH and DG) separately used this information to complete a quality assessment of each study using the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) (See ). Any inter-observer discrepancies between reviewers during the screening process were resolved at the ultimate stage via reviewer consensus.
2.4. Analysis
To categorise, analyse, and compare the studies involved in this systematic review, guidance for narrative synthesis by Popay et al. was followed [37]. The papers included in this review were summarised and ordered into groups in keeping with the theme.
3. Results
Applying the search methods outlined above, a sum of 501 studies was extracted. This was reduced to 351 once duplicates were removed. The PRISMA Flow Diagram, illustrating the progression of study selection, is shown in Figure 1 [34]. A detailed summary of all included studies (n = 28), the specific methods they used to measure pain and anxiety, and the relevant results is shown in . shows a more condensed and readily understandable synopsis focussing on the overarching main findings.
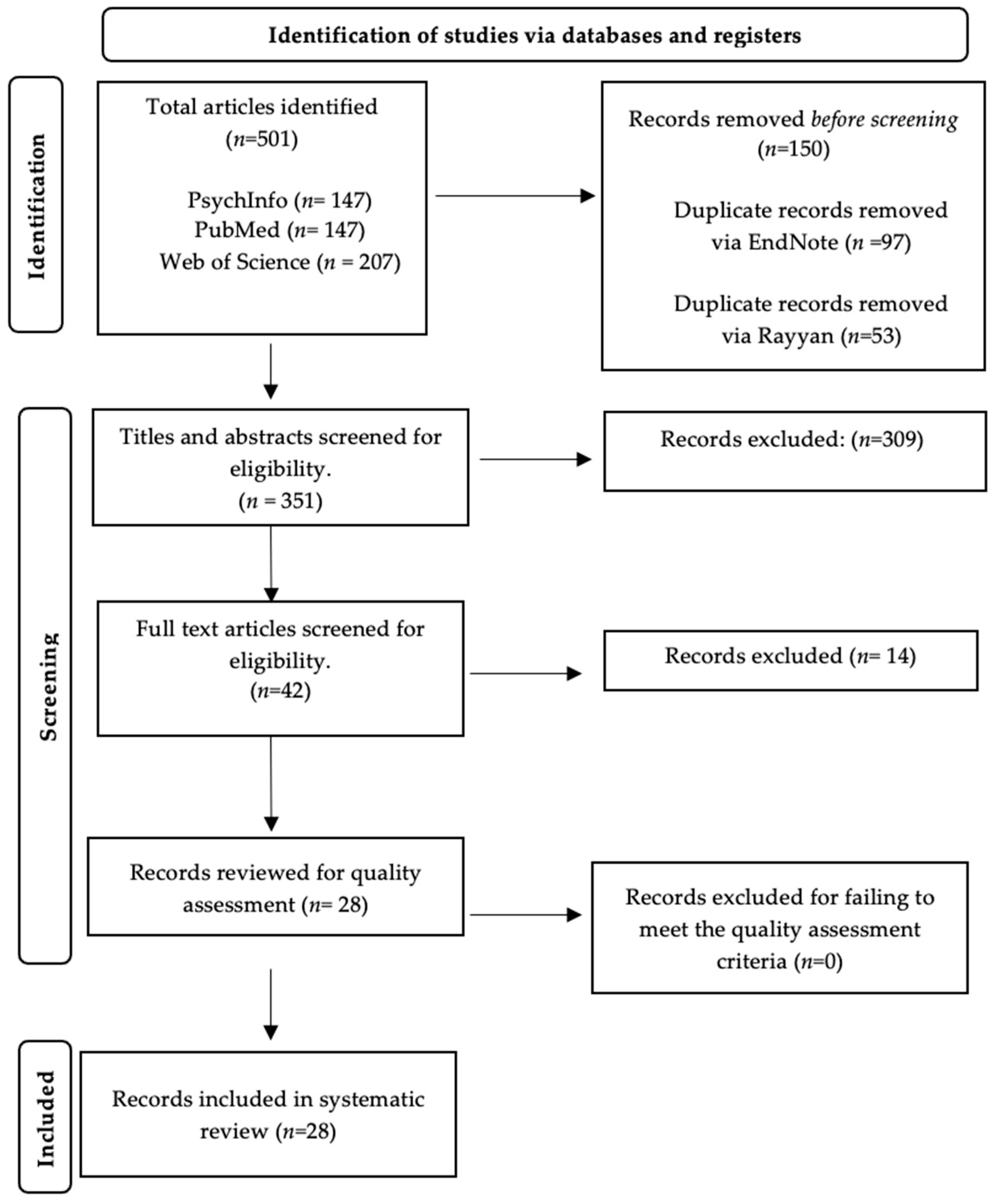
Figure 1. PRISMA Flow Diagram.
3.1. Studies Examining the Effects of Music-Based Interventions during Vaginal Labour
3.2. Studies Investigating the Effects of Music-Based Interventions during Caesarean Sections
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Results
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and narrative synthesis to explore the effectiveness of music-based interventions during vaginal labour and caesarean delivery using only RCTs. The literature search generated 28 studies, with a sum of 3835 participants included in the final evaluation. The extracted studies were grouped into two broad categories: studies examining the effects of music-based interventions during vaginal labour and studies investigating the effects of music-based interventions during caesarean section.
In summary, this review showed that most but not all the included studies found that music was beneficial in reducing pain and anxiety during vaginal labour [3,27,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,48,49,50,51,52,53] and C-section [13,14,56,57,59,60,61], particularly in primiparous women. However, other studies did not find a significant advantage of music over a control condition or a different therapy [47,58,60].
The application of music as one element of a larger treatment during vaginal labour [27,53], as individually selected music [41,52,54,55], as music combined with another therapy [27,51,52,53], as instrumental [3,14,40,43,46,48], classical [13,42,53] and relaxing [27,42,45,50,51,57,59,60] styles of music, and as music played via headphones during the caesarean procedure [14,54,57,59,60,61] all seemed particularly helpful in reducing pain and anxiety in mothers.
However, some studies revealed that the analgesic effects of music diminished as labour progressed [3,38]. Two studies found that music did not improve anxiety post C-section [5,54] and music, whilst effective during labour, may lead to increased anxiety 2 days postpartum [41]. Although music was effective at relieving pain and anxiety, massage [47,49], acupressure [51], and a combination of dance and music [52] were found to be more efficacious.
Thus, overall, music seems to be beneficial in reducing pain and anxiety during vaginal labour and C-section. It appears that this therapeutic effect can be amplified by combining music with massage, acupressure, or dance. However, the long-term effects of music during childbirth and C-section are not clear.
4.2. Comparison with the Results of Previous Systematic Reviews
The results of our review are mostly consistent with findings from previous systematic reviews that suggest that music is an effective method of pain and anxiety relief during childbirth.
Previous systematic reviews reported meta-analyses evaluating the impact of music on pain and anxiety during labour; however, they faced challenges stemming from the heterogeneity in methodologies in music intervention studies. In a systematic review by Chuang et al. [28], a meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the effects of music on pain and anxiety management during labour. While individual studies in the review indicated that music played during childbirth alleviated pain, the aggregation of results revealed considerable heterogeneity and a lack of statistical significance. Given these challenges and the variances in methodologies and outcomes in the existing literature, a narrative synthesis seemed a more appropriate approach for our study. This method of analysis allowed for a nuanced examination of the various methodologies and outcomes, ultimately yielding valuable insights beyond the scope of a traditional meta-analysis.
The results of our study indicated that the pain-alleviating effects of music during vaginal labour became less effective as labour progressed. This finding contrasts with a prior systematic review by Santiváñez-Acosta et al. [29], which assessed the effects of music on pain and anxiety management in primiparous women during labour and found that music alleviated pain throughout the latent and active phases of labour.
Our study also extended the findings of Weingarten et al.’s systematic review and meta-analysis, which examined the effects of music played during caesarean delivery on the mothers’ anxiety levels [31]. Both our study and Weingarten et al.’s study recognized the positive impact of music played during the intraoperative period. However, our research further emphasized the specific advantage of using headphones in this context.
Another systematic review by Lin et al. [30] included studies that assessed the anxiety-relieving effects of music in women undergoing a caesarean delivery or vaginal labour. The authors identified a general reduction in anxiety rates within the intervention group; however, they did not categorize the data based on the mode of delivery. Our study categorized and analysed the studies based on the mode of childbirth and therefore demonstrates a methodological improvement as it allows for a more accurate and contextually relevant assessment of the impact of music interventions on anxiety during childbirth, which may be of significant importance for healthcare practitioners and decision-makers.
4.3. Limitations of Included Studies
The heterogeneity in methodologies in the included studies makes it challenging to formulate overarching conclusions regarding the effects of music on pain and anxiety during childbirth.
One drawback is the inherent bias in studies employing music-based interventions resulting from the inability to blind participants and researchers to the condition to which they are assigned. Moreover, assessing the effectiveness of music interventions can prove difficult due to the multifaceted nature of music. Some studies did not follow the guidelines for reporting the type of music correctly as advised in the reporting guidelines for music-based interventions [62]. For example, some studies did not state the specific genre/songs or did not give their reasoning for the music chosen. Some participants wore headphones [3,14,40,48,49,50,52,54,57,58,59,60] whilst others did not [41,43,44,45,55,56], which can impact the listening experience, and MT was delivered by a trained music therapist in only two studies [27,45]. Previous research has emphasised the importance of a trained music therapist delivering music interventions for optimal effectiveness [63] as the lack of reported detail and variability in the quality of those delivering music interventions to participants may restrict replicability and the potential of implementing the outcomes in clinical practice. However, under real-world conditions, music is available almost everywhere at no additional costs, whereas music therapists are not always available.
Another limitation is that most of these studies did not assess participants’ music-listening habits or preferences prior to the interventions. What may be relaxing for one individual can be distracting/agitating for another, thus participants may not experience the intended pain-and-anxiety-relieving benefits of the intervention. Further, the birth and delivery processes are very dynamic and can result in the needs of the mother changing from needing music that is relaxing to music that may serve as a distraction from pain, discomfort, and anxiety. This can result in the patient wanting and needing different music for the different stages of birth and delivery.
Furthermore, many of the studies included in the analysis had small sample sizes, and none compared the pain-and-anxiety-alleviating effects of different genres of music. These factors increase the risk of overgeneralising the findings and leave gaps in our understanding.
None of the included studies measured/reported on the potential side effects of listening to music during childbirth. A previous study reported that music can elicit negative emotions and memories [64], which may amplify the pain and anxiety felt by participants. Music can also induce an ‘earworm’ i.e., involuntary repetition of music in an individual’s mind. This phenomenon can be distracting and distressing for the individual [65] and thus acts as a confounding variable in the included studies.
Additionally, most of the included studies used subjective ratings of pain and anxiety. Due to the intensity of labour, some individuals may find it challenging to accurately articulate their pain and anxiety levels, especially during peak moments of distress. Furthermore, trying to recall pain and anxiety post-delivery may result in inaccurate assessments and recall bias (Niven et al., 2000), consequently affecting the validity of findings. Two studies assessed the effects of music as part of a larger intervention [27,53]; however, it is unclear whether it was the music that was effective, or whether it was the additional components of the therapy that led to a reduction in anxiety and pain scores.
None of the included studies reported any long-term follow-ups, for example, one year post-childbirth. This information could be significant in steering the development of more efficacious and targeted music interventions going forward. Furthermore, no study compared the effect of music with the effect of medication during childbirth, and similarly, none of the included studies measured the effects of music on the accompanying person, who is often the father. The birthing partner is crucial as they can have a relaxing and positive influence on the mother, or they might panic and cause additional stress for the mother and professionals during childbirth.
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of the Current Review
This is the first systematic review to conduct a narrative synthesis to assess the effects of music-based interventions on both vaginal and caesarean deliveries exclusively using high-quality evidence from RCTs. Moreover, this systematic review analysed the effects of various methods of music selection, i.e., participant-selected, researcher-pre-selected, and participant-selected prespecified music. This approach offers a comprehensive insight into how various methods of music selection can impact outcomes, thus increasing the richness of the findings.
This review had several limitations. First, although extensive measures were taken to uphold academic excellence, the subjective nature of a narrative synthesis meant that we were unable to quantify our data and draw precise conclusions. As there were substantial heterogeneities between studies based on the study design, the group of study participants, the music intervention, and the outcome parameters, a meta-analysis was not possible. Moreover, most of the included studies were conducted in Europe [39,40,41,42,43,44,46,47,52,53,55,56,59] and Asia [3,13,14,27,38,49,50,51,57,61]. No study assessed the effect of music during labour in Africa or South America, therefore the findings of this review may lack external validity.
We planned to include only studies published in English or German. This approach might have increased the language bias and may have impacted the generalisability of the findings. In fact, there was no German article that fulfilled all the inclusion criteria. The only study from Germany included in this systematic review (Hepp et al., 2018) was published in English. There are several potential reasons for this, for example, most German studies on music therapy do not report RCTs, and many German journals that would report music therapy studies, e.g., the Musiktherapeutische Umschau, are not included in any of the three databases we used.
Another limitation is that no manual searching was undertaken. Relying exclusively on electronic database searches can result in overlooking relevant studies that are not indexed or easily obtainable online.
The protocol for this systematic review was not registered on PROSPERO, even though this would have increased the transparency of this work.
We did not differentiate between the therapeutic application of music facilitated by any clinician and music therapy facilitated by a professional music therapist. In , we used the wording from the original manuscript and did not make judgements about whether the music intervention fulfilled specific criteria that would justify the use of the term “music therapy”.
4.5. Implications and Future Directions
The results of this systematic review demonstrate that music-based interventions provide therapeutic benefits for pain and anxiety management during childbirth. It is therefore advisable that midwives and neonatal nurses consider incorporating music into the birthing process due to the psychological and physiological benefits for mothers. It might also be advisable that they consult a trained music therapist, when possible, to ensure appropriate and safe implementation of music-based interventions.
Building on insights gained from this systematic review, future research should consider studying the effects of specific music genres on pain and anxiety in mothers during childbirth. Different music genres can induce varying emotional/physiological responses. This nuanced approach would allow researchers to better understand the influence of music on maternal anxiety and pain perception during labour, ultimately enabling the development of tailored, culturally relevant interventions for mothers.
Additionally, no study has compared the effects/side effects of music with the effects/side effects of medication, including benzodiazepines or pain medication. Whilst it may be that acute pain and anxiety management is not possible and that music could potentially serve as a preventative means of mitigating severe pain and anxiety when introduced early, these assumptions need rigorous empirical validation.
Additional areas for the use of music during the perinatal period might include the effects of music or MT on potentially traumatic experiences of birth [66].
Future research should adhere to reporting guidelines for music-based interventions [62]. This methodology would facilitate more robust evaluations of music-based interventions, ultimately contributing to the execution of higher-quality systematic reviews with reduced heterogeneity. Long-term follow-ups and assessments of potential side effects of music are also recommended in future studies to strengthen the evidence supporting music-based interventions on pain and anxiety in mothers during labour. It would also be useful to investigate the added effect and health-economic value of a trained music therapist.
Finally, future research should also consider assessing the effects of music-based interventions in specific birth settings such as home births, hospital births, and birthing centres.
5. Conclusions
The current systematic review is the first to narratively synthesise the use of music-based interventions as a method of pain and anxiety relief for mothers during vaginal and caesarean deliveries. This review builds upon previous studies, illustrating that music interventions can alleviate pain and anxiety during childbirth and lead to improvements in physiological factors, including HR and BP. Participant-selected music, instrumental/relaxing styles of music, and music as part of larger interventions/combined with another non-pharmacological therapy appeared particularly useful. However, the findings suggest that the therapeutic benefit of music might apply primarily to alleviating low-level pain rather than acute pain. Additionally, to ensure the efficacy and safety of these interventions in clinical practice, further research is needed to assess the long-term effects and potential side effects of such interventions in the obstetric setting, along with implementing more rigorous methodologies such as following reporting guidelines for music interventions [62] and enlisting trained music therapists for intervention delivery.
References
- Hutchison, J.; Mahdy, H.; Hutchison, J. Stages of Labor; StatPearls Publishing LLC: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Whitburn, L.Y.; Jones, L.; Davey, M.A.; Small, R. The meaning of labour pain: How the social environment and other contextual factors shape women’s experiences. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2017, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phumdoung, S.; Good, M. Music reduces sensation and distress of labor pain. Pain. Manag. Nurs. 2003, 4, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott, D.; Papastefanou, I.; Paraschiv, D.; Clark, K.; Kametas, N.A. Longitudinal maternal hemodynamics in pregnancies affected by fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 49, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habanananda, T. Non-pharmacological pain relief in labour. J. Med. Assoc. Thai 2004, 87, S194–S202. [Google Scholar]
- Lukasse, M.; Hovda, I.; Thommessen, S.A.O.; McAuley, S.; Morrison, M. Oxytocin and emergency caesarean section in a medium-sized hospital in Pakistan: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Midwifery 2020, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, M.; Aksoy, A.; Dostbil, A.; Celik, M.; Ince, I. The relationship between fear of childbirth and women’s knowledge about painless childbirth. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2014, 2014, 274303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baljon, K.J.; Romli, M.H.; Ismail, A.; Lee, K.; Chew, B.H. Effectiveness of breathing exercises, foot reflexology and massage (BRM) on maternal and newborn outcomes among primigravidae in Saudi Arabia: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Womens Health 2022, 14, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafayi, M.; Imani, B.; Zandi, S.; Rabie, S. Comparing early postoperative maternal complications in elective and emergency cesarean sections. J. Midwifery Reprod. Health 2020, 8, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar]
- Safari-Moradabadi, A.; Hassani, L.; Ghanbarnejad, A.; Madani, A.; Rajae, I.M.; Dadipoor, S. The effect of education on knowledge and preferred method of delivery in nulliparous women. J. Health Care 2014, 16, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ferede, Y.A.; Bizuneh, Y.B.; Workie, M.M.; Admass, B.A. “Prevalence and associated factors of preoperative anxiety among obstetric patients who underwent cesarean section”: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 74, 103272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, K.; Coonan, T.; Ottaway, A.; Dutton, R.P.; Nuevo, F.R.; Gathuya, Z.; Wilson, I.H. Anesthesia and perioperative care. In Essential Surgery, 3rd ed.; Debas, H.T., Donkor, P., Gawande, A., Jamison, D.T., Kruk, M.E., Mock, C.N., Eds.; World Bank Group: Washington, WA, USA, 2015; Chapter 15; Volume 1, pp. 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Y. Preoperative music intervention for patients undergoing cesarean delivery. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2012, 119, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarghoee, S.N.; Mardani, A.; Baha, R.; Aghdam, N.F.; Khajeh, M.; Eskandari, F.; Vaismoradi, M. Effects of Benson relaxation technique and music therapy on the anxiety of primiparous women prior to cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 9986587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaal, N.K.; Hepp, P.; Heil, M.; Wolf, O.T.; Hagenbeck, C.; Fleisch, M.; Fehm, T. Perioperative anxiety and length of hospital stay after caesarean section—A cohort study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 248, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, S.; Jones, D.; Peach, M.J.; Gurrin, L.C. Anxiety in patients having caesarean section under regional anaesthesia: A questionnaire and pilot study. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2001, 10, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, I.; Fuchs, P.; Fuchs, A.; Lorek, M.; Tobolska-Lorek, D.; Sikora, J. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods of labour pain relief—Establishment of effectiveness and comparison. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanji, J.A.; Carvalho, B. Pain management during labor and vaginal birth. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 67, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, G.; Feeley, C.; Moran, V.H.; Downe, S.; Oladapo, O.T. Women’s experiences of pharmacological and non-pharmacological pain relief methods for labour and childbirth: A qualitative systematic review. Reprod. Health 2019, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, A.J.; Gabrielloni, M.C.; Rodney, P.; Barbieri, M. Non-pharmacological interventions during childbirth for pain relief, anxiety, and neuroendocrine stress parameters: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2018, 24, e12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfilippo, K.R.M.; Stewart, L.; Glover, V. How music may support perinatal mental health: An overview. Arch. Womens Ment. Health 2021, 24, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, R. Music, health, and well-being: A review. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-Being 2013, 8, 20635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situmorang, D.D.B. Dancing during labor in the midst of COVID-19 outbreak: As an alternative non-pharmacological treatment after digital interventions. J. Public Health 2022, 44, e617–e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, N.; Angeline, A. Effectiveness of music therapy on anxiety and pain among mothers during first stage of labour in selected hospitals at Kollam. Int. J. Nurs. Educ. Scholarsh. 2017, 9, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, T.; Viswanath, L. Effect of music therapy on labor pain among women in active labor admitted in tertiary care hospital Kochi. Int. J. Integr. Med. Sci. 2016, 3, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, P.; Bolding, A. Update on nonpharmacologic approaches to relieve labor pain and prevent suffering. Midwifery Womens Health 2004, 49, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Que, M.; Shen, J.; Nie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Jin, A. Effect of music therapy combined with free position delivery on labor pain and birth outcomes. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2022, 2022, 8963656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.H.; Chen, P.C.; Lee, C.S.; Chen, C.H.; Tu, Y.K.; Wu, S.C. Music intervention for pain and anxiety management of the primiparous women during labour: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2019, 75, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiváñez-Acosta, R.; Tapia-López, E.; Santero, M. Music therapy in pain and anxiety management during Labor: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. Medicina 2020, 56, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chou, H.H.; Chang, C.P.; Huang, M.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Lei, W.T.; Yeh, T.L. Effect of music interventions on anxiety during labor: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, S.; Levy, A.T.; Berghella, V. The effect of music on anxiety in women undergoing cesarean delivery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2021, 3, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariton, E.; Locascio, J.J. Randomised controlled trials—The gold standard for effectiveness research. BJOG 2018, 125, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, C.H. The effects of music listening on psychosocial stress and maternal–Fetal attachment during pregnancy. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saimbert, M. Keyprinciples for searching the literature. In Comprehensive Systematic Review for Advanced Practice Nursing, 2nd ed.; Holly, C., Salmond, S.W., Saimbert, M.K., Eds.; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Chapter 5; pp. 77–104. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.D.; Quatman, C.E.; Manring, M.M.; Siston, R.A.; Flanigan, D.C. How to write a systematic review. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 42, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popay, J.; Roberts, H.; Sowden, A.; Petticrew, M.; Arai, L.; Rodgers, M.; Britten, N.; Roen, K.; Duffy, S. Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. Prod. ESRC Methods Programme Version 2006, 1, b92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Chen, C.H. Effects of music therapy on labour pain and anxiety in Taiwanese first-time mothers. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simavli, S.; Kaygusuz, I.; Gumus, I.I.; Usluogullari, B.; Yildirim, M.; Kafali, H. Effect of music therapy during vaginal delivery on postpartum pain relief and mental health. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 156, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surucu, S.G.; Öztürk, M.; Vurgeç, B.A.; Alan, S.; Akbas, M. The effect of music on pain and anxiety of women during labour on first time pregnancy: A study from Turkey. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2018, 30, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buglione, A.; Saccone, G.; Mas, M.; Raffone, A.; Di Meglio, L.; di Meglio, L.; Toscano, P.; Travaglino, A.; Zapparella, R.; Duval, M.; et al. Effect of music on labor and delivery in nulliparous singleton pregnancies: A randomized clinical trial. Arch. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 301, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simavli, S.; Gumus, I.I.; Kaygusuz, I.; Yildirim, M.; Usluogullari, B.; Kafali, H. Effect of music on labor pain relief, anxiety level and postpartum analgesic requirement: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2014, 78, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, J.; Ventura-Miranda, M.I.; Requena, M.; Parrón-Carreño, T.; Rodríguez, R.A. Effects of prenatal music stimulation on state/trait anxiety in full-term pregnancy and its influence on childbirth: A randomized controlled trial. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 31, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanak, K. The effect of the sound of the ney (reed flute) on women in labour in Bursa, Turkey. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1934–1937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Browning, C.A. Music therapy in childbirth: Research in practice. Music. Ther. Perspects 2001, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, J.; Ventura-Miranda, M.I.; Requena, M.; Parrón-Carreño, T.; Alarcón, R. State-trait anxiety levels during pregnancy and foetal parameters following intervention with music therapy. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 232, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimber, L.; McNabb, M.; Court, C.; Haines, A.; Brocklehurst, P. Massage or music for pain relief in labour: A pilot randomised placebo controlled trial. Eur. J. Pain. 2008, 12, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella-Juarez, F.; Requena, M.; García-González, J.; López-Villén, A.; Alarcón, R. Effect of virtual reality and music therapy on the physiologic parameters of pregnant women and fetuses and on anxiety levels: A randomized controlled trial. J. Midwifery Womens Health 2022, 68, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghinejad, H.; Delpisheh, A.; Suhrabi, Z. Comparison between massage and music therapies to relieve the severity of labor pain. Women’s Health 2010, 6, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehcheshmeh, F.S.; Rafiei, H. Complementary and alternative therapies to relieve labor pain: A comparative study between music therapy and Hoku point ice massage. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2015, 21, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Wen, F.Y. Effects of acupressure and music therapy on reducing labor pain. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 898–903. [Google Scholar]
- Gönenç, İ.M.; Dikmen, H.A. Effects of dance and music on pain and fear during childbirth. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2020, 49, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perković, R.; Dević, K.; Hrkać, A.; Šaravanja, N.; Tomić, V.; Krišto, B.; Dukić, H.; Vasilj, V. Relationship between education of pregnant women and listening to classical music with the experience of pain in childbirth and the occurrence of psychological symptoms in puerperium. Psychiatr. Danub. 2021, 33, 260–270. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Bansal, G.L.; Sreehari, S.; Shukla, V.; Harsh, H.K.; Pareek, R. The effect of music on serum cortisol levels and anxiety in patients undergoing lower segment cesarean section under spinal anesthesia: A randomized controlled interventional study. J. Obstet. Anaesth. Crit. Care 2023, 13, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Eren, H.; Sahiner, N.C.; Bal, M.D.; Dişsiz, M. Effects of music during multiple cesarean section delivery. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2018, 28, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, P.; Hagenbeck, C.; Gilles, J.; Wolf, O.T.; Goertz, W.; Janni, W.; Balan, P.; Fleisch, M.; Fehm, T.; Schaal, N.K. Effects of music intervention during caesarean delivery on anxiety and stress of the mother a controlled, randomised study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Chen, C.H. Effects of music therapy on women’s physiologic measures, anxiety, and satisfaction during cesarean delivery. Res. Nurs. Health 2005, 28, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denney, J.M.; Blackburn, K.L.; Bleach, C.C.; Martinez, A.R.; Philips, J.B.; Lanier, K.; Dean, L.; Mertz, H. The effects of music intervention on women’s anxiety before and after cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled trial. Music. Med. 2018, 10, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horasanlı, J.E.; Demirbaş, N. Effects of music intervention during cesarean section on the level of the mother’s anxiety: A randomized controlled study. Erciyes Med. J. 2022, 44, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, M.S.; Gasti, V. Intraoperative meditation music as an adjunct to subarachnoid block for the improvement of postoperative outcomes following cesarean section: A randomized placebo-controlled comparative study. Anesth. Essays Res. 2018, 12, 618. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, A.; Kumar, A.; Hariharan, U.; Manjhi, B. Effect of perioperative music therapy/medicine on postoperative pain in women undergoing elective lower segment caesarean section delivery under spinal anaesthesia: A case-control study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2022, 16, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, S.L.; Carpenter, J.S.; Burns, D.S. Reporting guidelines for music-based interventions. J. Health Psychol. 2010, 16, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouffer, J.W.; Shirk, B.; Polomano, R.C. Practice guidelines for music interventions with hospitalized pediatric patients. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2007, 22, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Priya, A.; Applewhite, B.; Au, K.; Oyeleye, O.; Walton, E.; Norton, C.; Patsalos, O.; Cardi, V.; Himmerich, H. Attitudes surrounding music of patients with anorexia nervosa: A survey-based mixed-methods analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 639202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.P.A.; Applewhite, B.; Heiderscheit, A.; Himmerich, H. A systematic review of scientific studies and case reports on music and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.; White, C.; Hall, H.; Hewitt, A. Women’s experiences of birth trauma: A scoping review. Women Birth. 2021, 34, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

